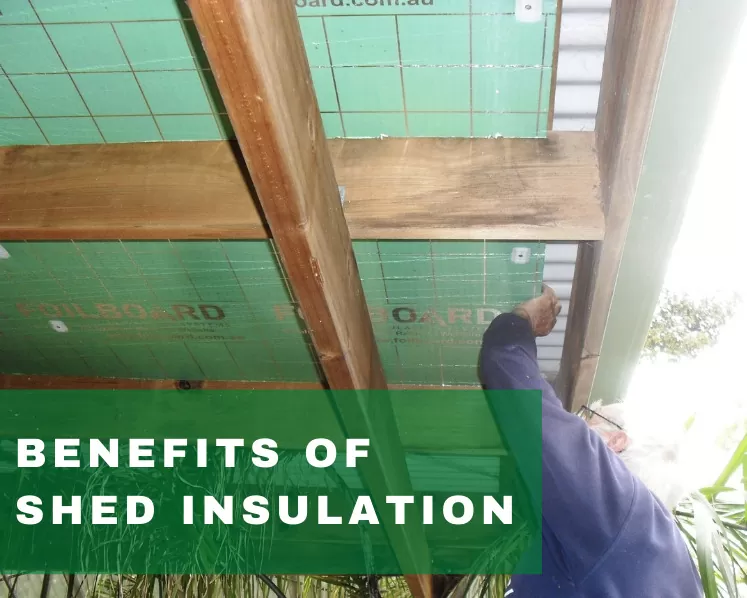
Insulating your home or office has never been easier than it is today. Not only are there a number of different materials available to choose from, but there are many different variations and installation options to suit the countless unique requirements that residents of homes, and property owners have. When it comes to the topic of insulation, the concept of the R value is one that is integral to the very fabric of the technology and its various applications.
In order for you to get the best out of your insulation, and ultimately, the optimum in thermal efficiency for your property, it is absolutely crucial to develop a thorough understanding of what exactly R values are, how they work, and how to determine what R value you specifically need for your property.
If you are looking at having insulation fitted in a new building, or alternatively, retrofitted in an existing one, you’ve come to the right place. If you’re reading this, then you are about to learn some very important and handy information about insulation and R values.
What is the R-value in Insulation?
To better understand the role of R values in the field of insulation technology, it pays to develop a better knowledge base regarding the basic purpose insulation serves by existing. Insulation’s primary function in any space is to increase the thermal efficiency of said space and regulate temperatures within. This means that insulation will keep the heat out of your home or office in the hotter summer months, and keep it in during the colder winter season. The way it does this is by minimising heat conduction, limiting its ability to flow from the external environment into your property, and vice versa.
Insulation sheets come in various different materials and structures, including foil, bulk, foam and more. The sheets themselves are not created equally. Each sheet is created with different R value ratings.
The R value is, in essence, the measurement of an insulation sheet’s ability to resist heat flow. Basically, R values range from 1.5 to 7, and the higher the number is, the more effective the insulation sheet is at increasing thermal efficiency, and thereby, insulating your home. Within the R value of insulation, there are three kinds of R values that are commonly used to more specifically measure heat flow resistance variables:
- The Down R Value: The down R value (also known as the summer R value) is a measurement of an insulation’s ability to resist heat flow from coming into the house. The reason it is sometimes called the summer R value is because, in summer, you want to keep the heat out.
- The Up R Value: The up R value (also known as the winter R value) is a measurement of an insulation’s ability resist heat flow from escaping the house. The reason it is sometimes referred to as the winter R value is because, in winter, you want to keep the heat in.
- The Total R Value: The total R value is, in most cases, what is referred to when you hear the blanket term ‘R Value’. It is a combination of the up and down R values.
What Insulation Has The Best R Value?
The easiest way to approach this question is to begin with the concept that there is no ‘best’ R value. Any insulation that carries a higher R value is going to be more effective than that with a lower R value, but the truth is that a higher R value is not always required for every home.
To appreciate this better, the BCA (Building Code of Australia) has within in it energy efficiency provisions for new homes, with requirements for certain R values. Different regions are broken up into ‘climate zones’, with each zone requiring a different minimum R value, based on its climate. For example, homes in climates that are extremely hot and humid only require R values of 3 or 4, while homes in freezing, alpine climates require a minimum R value of 6.
What R-Value Insulation Do You Need?
While the R value of 7 is more effective than the R value of 3, If you live in a home that is in a very hot climate, it would potentially be wasteful, unnecessarily expensive, and counterproductive to install insulation with an R value rating of 7. The best insulation is the one that suits your home and environment’s unique conditions the most effectively.
Types of Insulation and Their R Values
There are three very common and well trusted types of insulation:
- Foil Insulation: Foil insulation is a clever form of insulation that has a reflective surface on one side. It acts by deflecting radiant heat from the outside, back into the environment—which is why it is the best insulation for hot and sun-prone environments. The advantages of foil include that it is cost effective and easy to install. Foil insulation comes in a wide range of R values.
- Bulk Insulation: Easily the most popular and commonly used insulation around today, bulk insulation is designed with countless tiny air bubbles throughout the material, which it traps the hot air in. Rather than being made of just one material, bulk insulation comes in a range of different materials, including polyester, fibreglass, wool, recycled paper, and cellulose fibre. Bulk insulation too comes in a wide range of R values.
- Spray Insulation: A newer addition in insulation technology, spray insulation is made of foam and is surprisingly effective. As the name suggests, It is applied by being sprayed in the ceiling, floor, or in walls, and it expands into thick insulation. It is moisture resistant, but is also more flammable than traditional insulation, which is why we recommend it is installed by professionals only. A great advantage of spray insulation is that it has the ability to reach higher R values than any other insulation material.
How To Measure The R Value of Insulation
When manufacturers produce insulation, they do so with specific R values. So when you are buying insulation, consult your supplier to get more detailed information on what exact R value each insulation carries.
Insulation R Value Chart Australia
As discussed earlier, In Australia, the BCA has specified the R value requirements for all regions across the country. Here is a chart and map that details this information:
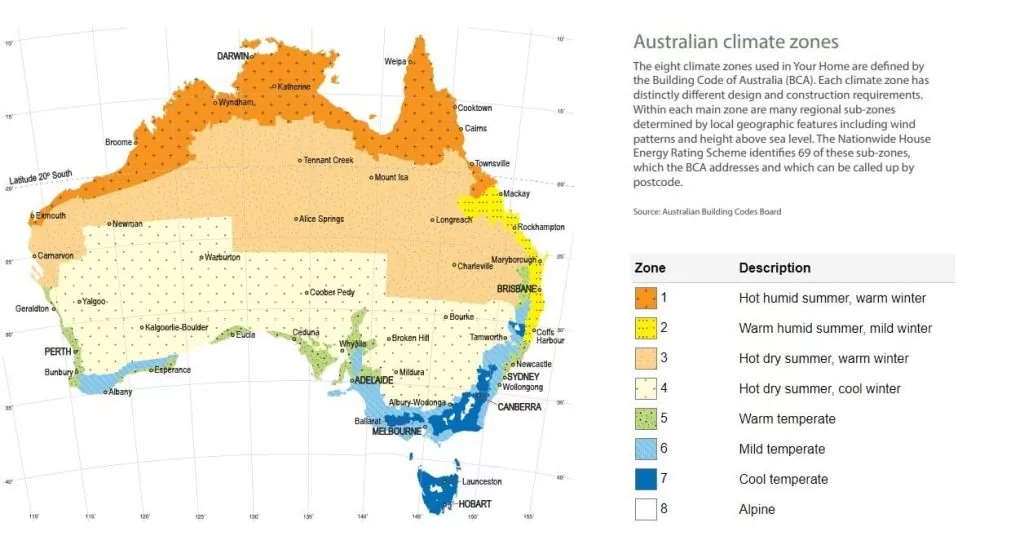
Zone 1 and 2 regions require lower R values of 3 or 4, while zones 3-7 require and R value of 5. As we reach zone 8, R values of 6 are required.
Selecting The Right Insulation
As you can see, R values have been well thought out to fit various climates and properties. While it can sound quite technical, if you have grasped the concepts discussed today, you will have a great understanding regarding the role R values play in your journey of selecting the right insulation—including the specific insulation material that suits you best.
If you would like to get insulation for your living space, or simply acquire more information about how it could benefit you—call us today on 1800 354 717.
How has this information shaped your understanding of insulation and R values? Let us know by leaving a comment below.